Predictive Planning and Analysis: A Practical Guide
- arun313
- Nov 28, 2025
- 3 min read
Modern businesses operate in an environment where decisions must be faster, smarter, and backed by data. Predictive planning helps organizations anticipate the future using historical data and algorithms—leading to more confident, proactive decision-making.
This guide explains predictive planning, the key analytical methods behind it, and how platforms like Jedox AIssisted™ Planning bring these capabilities into day-to-day business processes.
What Is Predictive Planning?
Predictive planning combines past data, statistical models, and machine learning algorithms to forecast future outcomes. Once the prediction is generated, business plans—budgets, staffing, inventory, production—are built around these expected values.
Where Predictive Planning Is Used
Across industries, predictive planning improves accuracy and agility:
Finance: Rolling forecasts, revenue prediction, expense modelling
Supply Chain: Demand forecasting, inventory optimization
HR: Workforce planning, hiring needs
Operations: Capacity, resource, and production planning
Sales: Pipeline forecasting, quota planning
Example:A company predicting next quarter’s sales using historical trends and seasonality can pre-adjust its inventory, marketing spend, and staffing. As new weekly or daily data comes in, the forecast updates automatically.
Core Methods Used in Predictive Planning
Predictive models typically fall into three categories:
Time Series Forecasting
Time series forecasting predicts future values based on data collected at regular intervals (daily, weekly, monthly).
It looks for patterns in:
Trend – upward or downward movement over time
Seasonality – recurring patterns (weekend dips, festive spikes)
Cycles – long-term business or economic cycles
Noise – random fluctuations
Common use cases:
Monthly revenue forecasting
Energy consumption prediction
Project duration estimates
Regression Models
Regression answers questions like:📌 “How much?”, “How many?”, “What will the numerical value be?”
Examples:
Future sales volumes
Budget needs
Manpower forecasting
Price prediction
Demand modelling
Regression identifies relationships between one or more drivers (inputs) and a target variable (output).
Classification Models
Classification answers:📌 “Which category?”, “Will it happen?”, “What class does this belong to?”
Examples:
Customer churn risk (High / Medium / Low)
Fraud detection
Inventory stock-out risk
Lead scoring and prioritization
Project success vs. failure
These models help businesses sort, categorize, and prioritize outcomes.
AIssisted™ Planning in Jedox
Jedox’s AIssisted Planning integrates predictive algorithms directly into planning workflows. It automates forecasting and provides wizards for:
Time series predictions
Driver-based forecasting
Classification
Data preparation
Driver analysis
Jedox can automatically select the best algorithm based on the input data—making predictive planning accessible to non-technical users.
Time Series Forecasting in Jedox
Prerequisites
Minimum 3 years of historical data
A model using a standard time dimension (Day/Week/Month)
A target version (e.g., Forecast)
A measure defined for storing forecast values
Process Overview (Wizard-Driven)
Source Setup
Select time range
Filter by dimensions such as version and measure

Target Setup
Choose forecast version
Select target measure
Define the number of months to predict
Recommended: Prediction type = “Best”
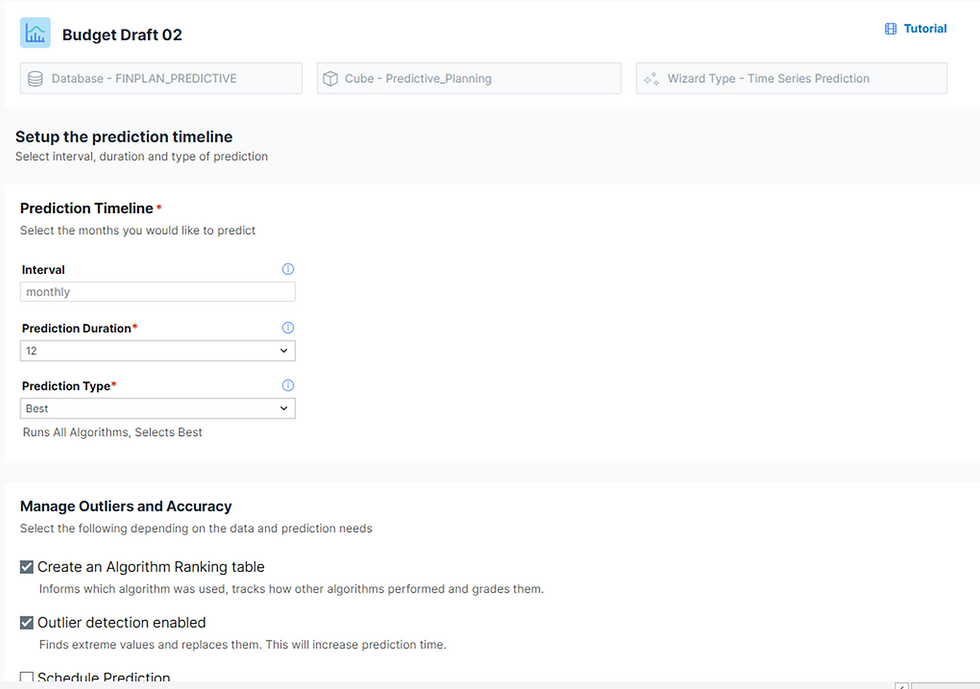
Review Selections
The wizard displays the chosen data and configurations.

Execution & Results
View forecast results with accuracy indicators
Automatically generated upper and lower variations
These trends can be used as a base for further planning

Driver-Based Prediction in Jedox
Driver-based modelling predicts outcomes based on selected causal factors (drivers).
Steps:
Select history and driver measure
Apply dimension filters
Choose target version and measure
Select number of forecast months
Recommended: Use “Best” prediction type
Remaining steps mirror the time series workflow.

Classification in Jedox
Classification helps categorize outcomes such as:
Risk level
Churn likelihood
Inventory shortage probability
Lead conversion probability
Setup Steps:
Select the time range
Choose the driver measure
Include influential attributes/dimensions
Set the target version and measure
Choose forecast period and prediction type


Data Preparation in Jedox
Real-world datasets often have missing or incomplete values. Jedox’s Data Preparation module helps fill gaps before forecasting.
Techniques:
Interpolation
Fills missing values within historical periods
Extrapolation
Predicts values for missing future periods
Example:If sales data is missing from Nov–Dec 2025, extrapolation can estimate those values based on prior trends.
Proper data preparation ensures higher accuracy across all prediction types.

Conclusion
Predictive planning transforms business decision-making from reactive to proactive. Using techniques like time series forecasting, regression, and classification—combined with tools such as Jedox AIssisted™ Planning—organizations can:




Comments